WELCOME TO HEAD & NECK ROBOTIC SURGERY
Advancing minimally invasive surgery with cutting-edge robotic systems for safer, faster, and more effective treatments.
The term Robotic Surgery can be misleading, as the majority of currently available systems still lack programmability or autonomy. At present, the term primarily pertains to remote systems utilized for soft-tissue surgery, enabling the remote execution of advanced endoscopic procedures. It is important to note that the surgeon remains the active participant in the surgical process, operating in a master-slave configuration interacting with the robotic device to carry out the procedure.
Numerous companies have devoted significant efforts over the years to develop diverse solutions in the field of robotic surgery, resulting in the introduction of numerous devices for clinical utilization. The details? See bellow.
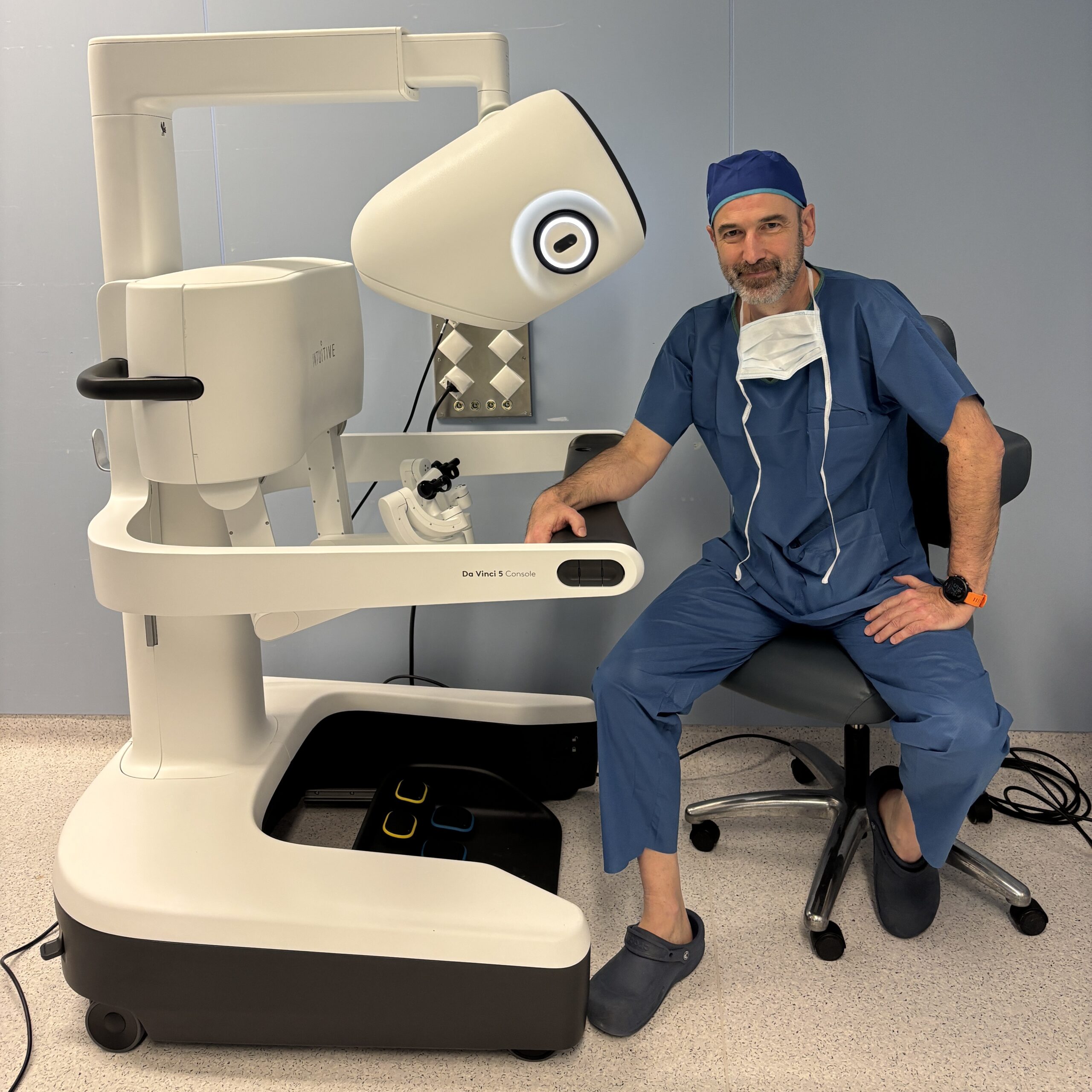
Whether you are a medical professional seeking in-depth knowledge or an individual interested in expanding your understanding, whether you seek to explore the nuances of robotic surgical systems, understand their benefits, or stay up-to-date with the latest industry trends, this website serves as a resource for gaining a deeper understanding of this rapidly evolving field.
There is a revolution going on. AI is reshaping the world as we know it. Nothing will remain the same. Where more tech is involved changes will be more radical. Medicine in general is a particular edge. And just see the logo of this web (Tech Improving Outcomes).
Everything is going very fast. The paragraph at the beginning of this page is still true, but it will not be for long. We will try to keep you updated here.
Related post:
Artificial Intelligence integration — for automated camera control, safety checks, and performance feedback.
Haptic feedback — restoring the surgeon’s sense of touch.
Miniaturised and flexible robots — for endoluminal and natural orifice surgery.
Tele-surgery — performing procedures at a distance via ultra-low latency networks.
